In e-commerce, every company should strive to minimize transit times, catalyze deliveries, and keep shipping expenses low. And if fulfillment optimization is your goal, it’s crucial to understand how shipping zones are defined—and how they’ll influence your overall fulfillment strategy.
Shipping zones can affect nearly every facet of your shipping strategy, whether your capacity, average delivery times, or overall shipping costs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the nine domestic shipping zones and discuss how to optimize your fulfillment model, no matter where your shipments need to be delivered.
What Are Shipping Zones?
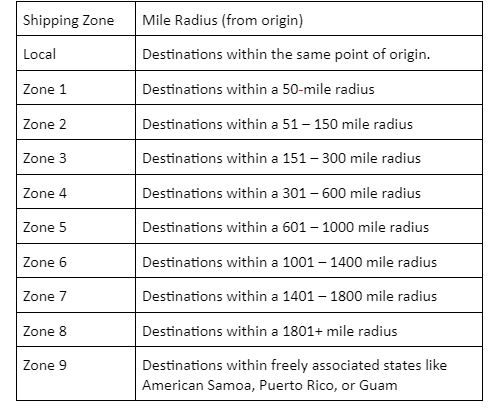
Shipping zones are geographical regions predominantly measured by the distance from a shipment’s point of origin to its ultimate terminus. They operate on two principles:
- The closer a customer is to you, the lower the zone, and the faster their package will arrive.
- The further a customer is from you, the higher the zone, and the longer a package will take to reach its final destination
In the US, domestic shipment zones span from Zone 1 to Zone 8—1, the closest and 8, the hardest to reach.
While most shipping carriers use a zoning method, every carrier’s shipping method is different. For example, the UPS shipping zone method can slightly vary from FedEx or USPS shipping zones.
But, Generally speaking, a Zone Map will appear as follows:
While distance is the primary gauge for designating zones, this distance is not measured in mileage but rather by zip code groupings.
For instance, it may be quicker to send a package from San Diego, CA, to New York, NY than from South Dakota to a rural location in West Virginia. While West Virginia is technically closer to South Dakota than New York to San Diego, sending a package to a location off the beaten distribution path can be more logistically complex for carriers.
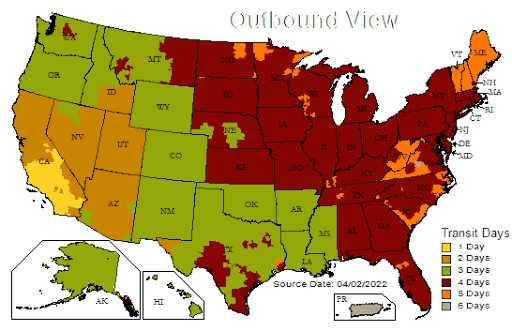
These intricacies may be easier to visualize by entering your business’ address in the UPS U.S. Ground Map.1 For example, the image below approximates how shipping zones would appear to a business located in San Diego, CA:
How to Determine Your Shipping Zone
If there’s one thing to remember about shipping zones, they aren’t set in stone. Shipping zones are dynamic and tied to your company location, which may differ significantly from business to business. Moreover, each carrier’s approach to zoning also varies.
Fortunately, it’s relatively simple to find out what your shipping zones are. First, visit the website of the carrier you want to use. From there, you can use their automated tools to calculate the shipping zone that corresponds with your shipment’s destination and estimated shipping costs.
For the three major shipping carriers in the US, just follow the following links:
How Do Shipping Zones Impact Your Business?
Every e-commerce business should know how shipping zones affect its business model and bottom line.
There are three main reasons you may feel the brunt of shipping zones: shipping costs, shipping weight, and your average time of fulfillment.
Shipping Costs
Most carriers will use zones to help determine the rates they’ll charge for shipping services. Generally, the further a package travels from its origin, the more it will cost.
Additionally, certain types of shipping services may be subject to zoning, whereas others aren’t. For example, while USPS Priority Mail Express is zoned, First-Class Mail isn’t. So, USPS zones will be used to determine a shipping rate for Priority Mail Express only.
For businesses that send shipments all over the country, understanding your per-package freight costs is essential for setting shipping prices for customers. If you select a standard charge for two-day shipping that’s too low, you could feel the pinch—especially if a significant portion of your customer base lives far away.
Shipment Weight
If you’re in the business of shipping heavier or bulkier items, sending shipments to higher shipping zones can have an even greater impact on pricing.
That said, there are ways to optimize your fulfillment strategy, reduce your zones, and lower your shipping costs. Instead of warehousing goods in a single location—particularly your heavier products—you can split them up into several locations across the country. That way, no matter where a customer lives, you can slash shipping expenses by sending the product from the shipping hub the fewest zones away from their location.
Fulfillment Times
As our handy UPS ground map demonstrates, higher zones simply take longer to reach.
If you promise all of your domestic customers a 2-day delivery on their orders, you’ll need to tailor your fulfillment strategy so that all of your merchandise is within range of your customers—in this case, 5 zones or less. If that’s not plausible for you as a business, you’ll need to amend your guarantee, so your shipping policies align with customer expectations.
Know Your Zones, Optimize Your Fulfillment
These days, the success and reputation of an e-commerce business depend on the integrity of its fulfillment strategy. Customers want their products as speedily as possible, and everybody wins when shipping costs—and logistics—are streamlined to a T.
While you can’t alter the country’s physical landscape, you can familiarize yourself with how shipping zones work. And with some industry know-how—and a competent shipping service—you can design a fulfillment strategy that meets your customer where they are without feeling the pinch in the process.
At Shipware, we can also help you reduce shipping costs and streamline your order fulfillment for better operations. Using audit and consulting services, we help ensure your parcel and LTL shipping is a smooth process. Contact us today to learn more!
Sources:
- UPS. U.S. Ground Maps. https://www.ups.com/maps/results?loc=en_US